- How to Remove 3D Print From Bed - May 31, 2022
- Autocad vs Inventor: Which Software is The Best? - April 5, 2022
- Autocad vs Revit [2022]: Which Is The Right Choice? - March 31, 2022
When you think of silicone and 3D printing, you’re more likely to consider it as a helping hand, rather than a star player.
Silicone is commonly used as a mold material into which other material is poured to make a 3D object. But that’s limiting this versatile compound and your imagination to go along with it – you can now 3D print with silicone as if it were any other type of printing filament.
It takes extra care and consideration to make sure you’ve got the right knowledge and equipment, so read on to find out what to look for and what to avoid when buying a 3D printer for silicone.
What is the best 3D printer in 2021? That entirely depends on what your application, or what you want to make, is. Whether you're looking for a reliable 3D printer for your business for rapid prototyping, or an educator looking to advance the way your students learn, MatterHackers can find the best 3D printer to fit your needs.
Table of Contents
What is silicone?
Silicone is the name given to a group of chemical polymers that are based on chains of alternation silicon and oxygen atoms. Organic groups are attached the to silicon atoms, and the resulting materials are generally resistant to chemical attack and not temperature sensitive.
These characteristics make silicone great for manufacturing and in particular for medical objects since those are exposed to all kinds of fluctuating conditions and environments.
How is silicone used in 3D printing?
Traditionally, silicone is used in a type of 3D manufacturing process called mold injection. That uses a mold to shape liquid into the objects desired, and silicone is great for that because of its tough yet flexible physical properties.
However, mold injection modeling has a very high upfront cost and does not have the ability to create small details as additive 3D printing does, so in 2016, Wacker Chemie made positive waves when it announced it had figured out a way to 3D print with silicone like you can with thermoplastics and metal compounds.
Soon after that, Envisiontec, Carbon 3D, and Fripp Design all jump in with their own contributions to equipment and material especially constructed to work with silicone.
Right now, the majority of usage for 3D printed silicone is still in the medical area, but the same advantages that make it great in that sector can easily translate to others, and if you’re jonesing to try it yourself, you totally can. We have the additive manufacturing technology!
What is the process of 3D printing with silicone?
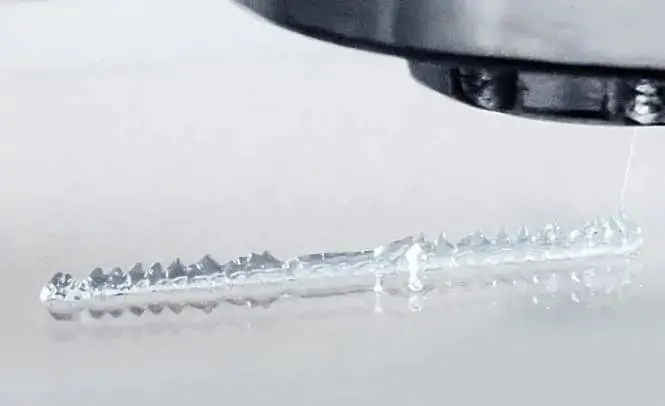
3D printing with silicone is a lot like printing with chocolate, and other materials that need to stay liquid during the printing process. Instead of a solid, threadlike filament feeding through an extruder, the silicone is melted and forced through the extruder in tiny drops, which are layered on top of each other (layer by layer) just like any other filament.
The printing process is still based on whatever you tell your computer to tell it – there’s no difference in your design process for additive manufacturing. So the extruder takes your design and maps out where to place the droplets and how close to put them together; it completes your creation through a 3D version of pointillism.
Then, there’s one last extra step you have to do for silicone to make it solidify and hold its shape in its firm yet flexible signature style. You have to vulcanize it.
Sounds terrifying, right? Don’t worry – this is just a fancy label for when silicone 3D printers make the silicone firm. It’s done with the sweep of a UV light in the printing area, which forms cross-links between sections of the polymer chain.
This hardens the silicone enough to keep its shape, and increases its durability in the face of structural stress. It’s a neat, no-fuss flourish to make sure your silicone 3D printed object stays unyielding in the important areas of its molecules.
What are the advantages of printing with silicone?
Silicone has a lot of great properties that you can take advantage of now that we’ve harnessed the power of it for 3D printing.
Strength and flexibility
Because of the science, we go into above; silicone is a super unique combination of strong and flexible. It will bend quite easily without breaking, which not only makes it able to withstand more pressure than something with more rigid connections but also makes it more portable, able to fold in on itself without any disassembling necessary.
This all comes through in your final 3D printed object without you having to do any extra or complicated step; silicone is just naturally awesome like that.
Bio-compatibility
One of the most famous uses for silicone is bodily implants, and there’s a great reason for that – silicone is not rejected by human tissue, so it’s perfect for reconstructing body parts that share its properties. It’s also great for objects that are not necessarily inside someone’s body but are in constant contact with skin or other vulnerable areas, like hearing aids, nose pads on the bridge of glasses, and respiration masks.
Temperature and radiation stability
Silicone can hold a temperature steady, so the area inside of a silicone shielded object does not feel the effects nearly as fast as under a non-temperature stable material such as glass. This same property makes silicone a good shield for radiation as well. The auto industry uses it a lot for engine parts that are exposed to massive temperature spikes as cars are turned on and used, such as hoses and plugs.
Transparency
Silicone’s see-through properties make it great for applications where vision is needed, but glass may be too fragile, such as the lenses in optical equipment. Whereas glass lenses are prone to scratches that are very difficult, if not impossible, to get out without changing the curated view of the lens, silicone lenses are less rigid and thus tend to not get as many scratches in the first place. If you’ve ever struggled to see out of an old pair of eyeglasses or tried to use a scratched touchscreen, you’ll appreciate the ability of silicone to stay smooth.
Electrical properties
Silicone can be both conductive and insulating, and that unique combination makes it great assistance for processes that need both, like securing fluids in hydraulic applications.
What are the disadvantages of printing with silicone?
Can’t return to its liquid state
One thing that is counter-intuitive but important to remember about silicone is that once it’s hardened into a solid, it can’t be melted down again without causing significant structural damage to its chemical makeup.
This is a feature that makes it great for final products, but if you make a mistake, there’s no chance to reshape or reuse the material, so be sure you either get it right on the first try, or you have more silicone available than is necessary for your project so you can try again if need be.
Special 3D printing equipment needed
As mentioned above, 3D printing with silicone is not like working with more traditional 3D printing material. With silicone, you have to have a special extruder that pulls the liquid silicone through the machine with a pump and extracts it like an inkjet printer onto the build surface.
There are a few other materials that need the same kind of treatment, so it’s not hard to find the right equipment, but if you have a rig meant for spooled filaments, you will need to buy an additional machine to print silicone.
Longer finishing process
Because objects that are 3D printed with silicone have a special hardening process, it takes longer to complete a project from start to finish, not ideal for rapid prototyping. The vulcanization process is fairly easy, requiring only a sweep of a UV light to stiffen the connections between the silicone molecules you’re working with, but be aware this may take more than one pass to complete.
If you’re used to working with materials that need cool down time after your object itself is printed, this would be roughly equivalent to that wait time, depending on the size of your silicone object. However, if you’re in an extreme hurry, you may need to choose a material that can go right off the printer bed.
Small production run
Silicone can help you manufacture a palette of cloned objects all at once – unfortunately, it can’t when you 3D print with it. As with all 3D printers, those that print with silicone are designed to produce one object at a time, which is what gives each object such a great capacity for details within the additive manufacturing process.
However, if you’re looking to 3D print with silicone to manufacture additive printed parts or objects on a large production scale, we recommend checking out the injection mold process instead (silicone mold).
Further Read: Injection Molding vs 3D Printing.
Not much documentation
New printing technology is always exciting, but it’s also prone to unexpected errors and quirks that haven’t had a chance to work themselves out yet. Since 3D printing with silicone materials is so recently developed, there is not a large body of documentation to study for print parameters before you start.
The information that is out there is from the companies who manufacture the printers capable of 3D printing with silicone; this is very useful, of course, but if you’re uncertain about 3D printing with silicone now, you may want to wait until it’s been around long enough to garner reviews and instruction documents from independent sources (like us!).
What do I need to look out for when buying equipment to 3D print with silicone?
If you are shopping for 3D printers to use with silicone, buy one with all of the following features:
- Inkjet extruder. This is how the silicone gets from your machine onto the print bed and into the shape of your object. A regular feeder extruder system is not going to work, so make sure you are aware of how the printer you’re eyeing works with the printing material you give it.
- Internal warmer and pump. Since silicone has to be liquid to be 3D printed, look for a machine that features both a warmer and a pump in its extruder workings. This will keep the silicone at a workable consistency while proactively moving it through the printer’s system at an even pace, so you don’t get clumps or nothing going through your nozzle.
- Short, straight pipeways from material to extruder. Once the silicone is heated and liquid enough for the extruder to work with, it’s going to need to travel the least amount of distance that is practical for it in the machine’s interior. Reducing the length and turns in its path means it will flow better and more evenly without needing external help to go through the system.
- Glass-enclosed printer bed. This can be a feature on 3D printers that don’t use silicone, but there, it’s usually a luxury. With silicone, it’s a necessity because of that extra final step of vulcanization that silicone requires before being ready to use as a 3D printed object. The glass chamber contains the UV lights that run over the silicone to harden it, so it’s a crucial feature for all of your 3D silicone printing needs
What are some recommended products for 3D printing with silicone?
Now that we’ve walked you through the process of 3D printing with silicone and explained what to look for when you’re ready to start, here are a few of our favorite products that help you ace working with this material.
Current Commercial 3D Printing Players
Note: Right now, most of what you get are printing services and 3d party manufacturing vs affordable desktop silicone printers.
- Wacker Chemie AG 3D printers for silicone. These guys literally invented this process, so their hardware is the standard by which all future 3D silicone printers will be judged. They’ve got customer 3D printing services as well, so if you’re not looking to buy a whole new printer for silicone, you can order silicone parts in a single quantity or a dozen from their offices and get the object without having to deal with your own machinery.
- Wacker Chemie AG silicones. To go with their printers, Wacker has developed a line of inorganic silicones that have more consistent chemical properties than organic silicones, so try some out for great quality prints.
- EnvisionTech 3D Bioplotter. This line of printers is made with medical application especially in mind. Its build environment is calibrated for the perfect UV light curing process, which is essential in finishing material meant for contact with delicate areas, like what medical implants tend to touch.
- Carbon 3D SIL 30 silicone. Carbon 3D has developed a type of silicone that is specifically designed to give your 3D prints all the pluses of silicone with a minimal amount of drawbacks. It can expand 330% before it even thinks about tearing, so it’s got top-notch flexibility and strength.
What’s the verdict for 3D printing with silicone?
Although you need a specific type of printer for 3D printing with silicone, it’s well worth the extra equipment.
Once you get your printer set up, the silicone will give your 3D printed objects all the strength, flexibility, transparency, electricity manipulation, and biocompatibility you could imagine, so we highly recommend trying this material for its awesome perks. And once you find a printer that can handle it, you’ll be good to go for life.
What is the best 3D printer in 2021? That entirely depends on what your application, or what you want to make, is. Whether you're looking for a reliable 3D printer for your business for rapid prototyping, or an educator looking to advance the way your students learn, MatterHackers can find the best 3D printer to fit your needs.
Recommended Reads
- Best 3D Printers for Nylon Printer Filament
- Best 3D Printers for Miniatures
- PETG vs ABS Filament Compared
- ABS vs PLA Filament Compared
- Creality CR 10 Review – Is It The Right Printer To Have?
- 5 Most Affordable 3D Printer Options [2020 Edition] – Best Budget 3D Printer
- The Best 3D Printer Hot Ends to Use [UPDATED for 2020]
- Wanhao Duplicator i3 Review

![How to Find the Best Silicone 3D Printer [2022]](https://total3dprinting.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/How-to-Find-the-Best-Silicone-3D-Printer.jpg.webp)