- How to Remove 3D Print From Bed - May 31, 2022
- Autocad vs Inventor: Which Software is The Best? - April 5, 2022
- Autocad vs Revit [2022]: Which Is The Right Choice? - March 31, 2022
Wax seems like the opposite of a good 3D printing material. Its defining property is how changeable it is, never quite hardening to settle into a definite shape, always moldable at the slightest push of a finger.
But, when we learned that you could, in fact, get great 3D printed objects from wax material and filament, we were very pleasantly surprised, even more so when we saw how easy it is if you have the right additive manufacturing equipment. We’re passing that knowledge on to you for your own personal enjoyment and use.
While most 3D printers CAN be modified for wax printing, some are better suited than others. To cut right to the chase, these are the best wax 3D printing options to produce optimal results…
Quickly drying resin based filament is key to maintaining structural integrity. Particularly for wax-style filaments, we use this system to prevent ambient moisture from corrupting the filament.
Table of Contents
Best Wax 3D Printers
These are the best 3D printers for wax:
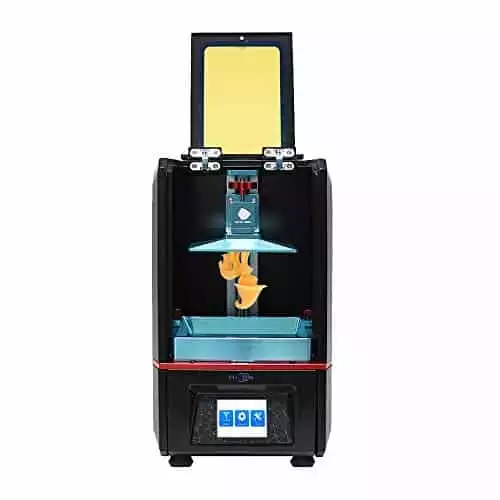
Anycubic Photon
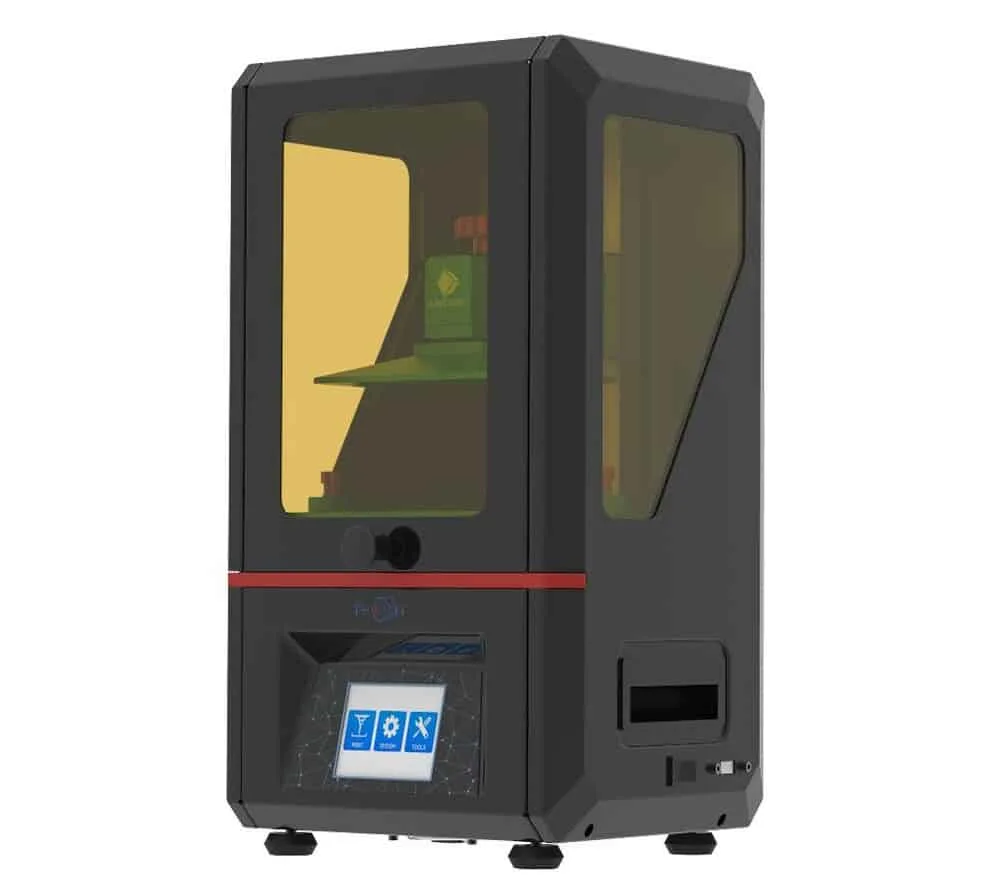

This is more of a budget friendly option. Very capable, great value for the money. Especially for this printer, we recommend investing in the PrintDry kit to rapidly dry to maintain structural integrity post printing. ALSO: some users report issues with the material not sticking to the smooth surface build plate.
In this case, use 80 grit sandpaper to coarsen the build plate and smear a layer of resin (not WaxCast) onto the build platform as a surface finish, then expose it to the sun for 5+ minutes. Recommended Wax Filament: MakerJuice WaxCast resin.
Dead simple to set-up, comes pre-assembled, intuitive touch-screen and exceptional level of detail. This machine empowers CREATORS, without expecting you to be a mechanic. The small - but precise - print bed is perfect for miniatures.
Peopoly Phenom MSLA 3D Printer
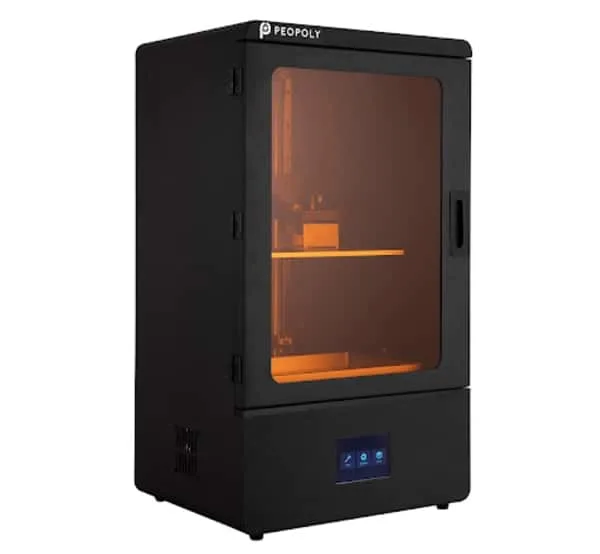

This is certainly a higher end unit (one of our favorites), but if you can swing the price, it’s the best option. As a resin-based 3D printer, it’s particularly adept with wax-like printing filaments. Recommended Wax Filament: MOLDLAY filament available here.
Check out the full Phenom review here.
Unfortunately the Phrozen Transform has had supply issues recently. It's out of stock everywhere! Instead, I recommend the Peopoly Phenom as an excellent (if not better) resin-based 3D printing beast.
Solidscape S390
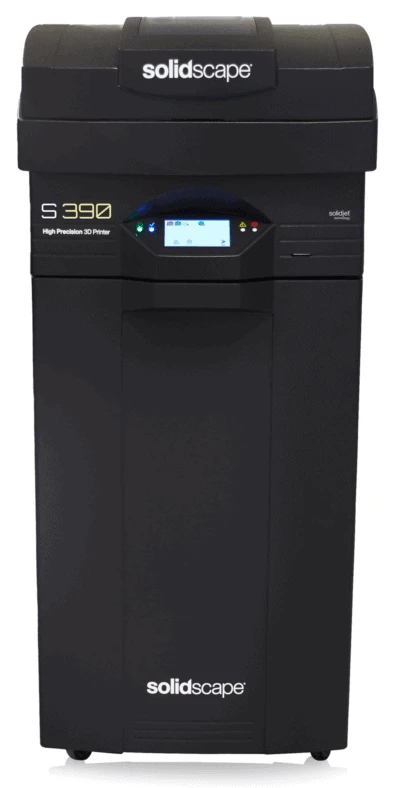

Built for jewelry makers, the Solidscape S390 is perfect for those who are looking for fast, accurate, and precise 3D models. You can use this 3D printer to create wax models that serve as casts for your jewelry.
The Solidscape S390 comes with a lifetime printhead warranty, so you’re never going to have to worry about that. You can choose from among five resolutions, from 25 to 50 micrometers.
This printer also delivers the sharpest details in any print. You can get castable models. Further, it comes with a power regulator built-in.
But this printer can be expensive for most people. However, if you are a serious jewelry designer or 3D printing professional, this will be a good addition to your arsenal.
Sindoh 3DWOX 1 Wax 3D Printer
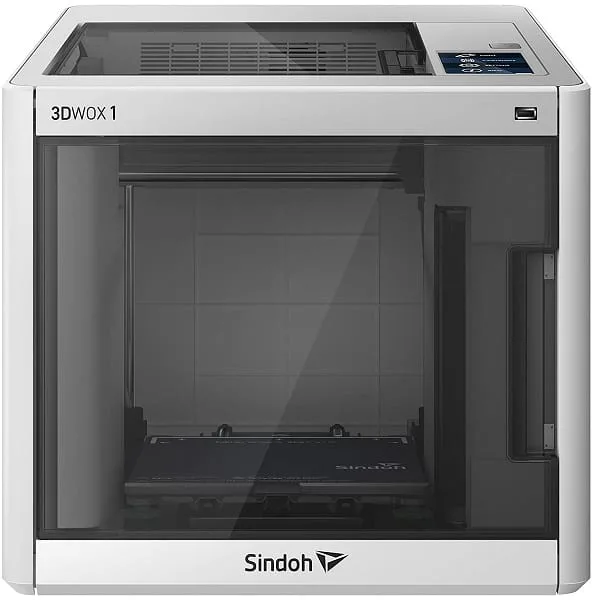

The Sindoh 3DWOX 1 Wax 3D Printer has a sizable build volume of 8.2 by 7.9 by 7.0 inches (210 by 200 by 195 millimeters). This printer works with third-party filaments, which allows you to use the material you want without worrying about where to get it.
It’s very easy to set this printer up with the assisted bed leveling feature. You can also load filament automatically.
The metal bed is very flexible. You don’t need to scrape the finished print off the bed. What’s more, the nozzle cleans itself.
This quiet worker also has a HEPA filter that helps deal with the fine particles created during printing.
Discover further 3D printing possibilities with this beauty. It offers a reliable flexible bed, fully automated loading, printing in silence and more.
Zortrax Inkspire
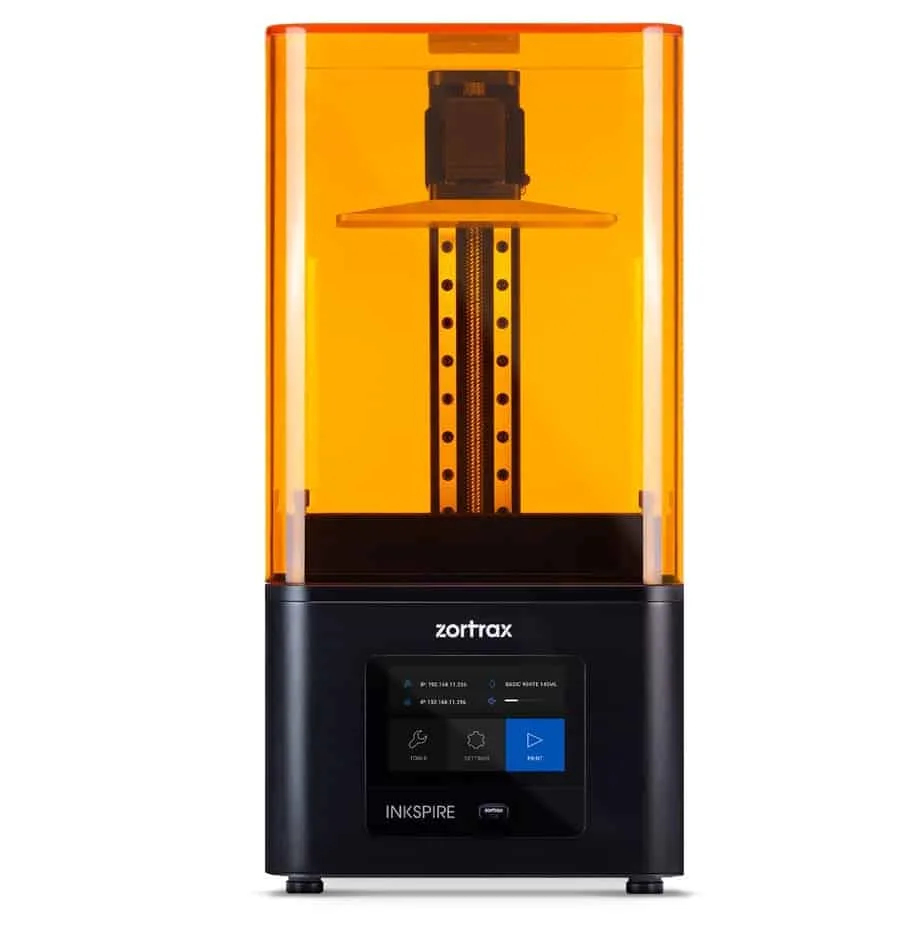

Zortrax Inkspire is a resin 3D printer that can print layers that are 25 microns thin. This machine is based on Android, so it’s easy to figure out. What’s more, calibrating the printer is semi-automatic.
If you need a 3D printer capable of churning out models with perfect details, then look no further. What’s more, the surfaces are flawless. Post-processing is almost unnecessary because it’s easy to remove the support structures.
You can print wax models of up to 5.2 by 2.9 by 6.9 inches (132 by 74 by 175 millimeters). This printer comes with a four-inch (101.6 millimeters) IPS touchscreen with 800 by 480 pixels resolutions. Connectivity options include USB, Ethernet, and Wi-Fi.
You can use third-party resins with this printer. However, the manufacturer does offer their BlueCast line of resins that can be used with the printer.
The Zortrax Inkspire UV LCD resin 3D printer creates small, detailed 3D printed parts that are perfect for projects like dental prosthetics, jewelry, or part production.
FormLabs Form 3
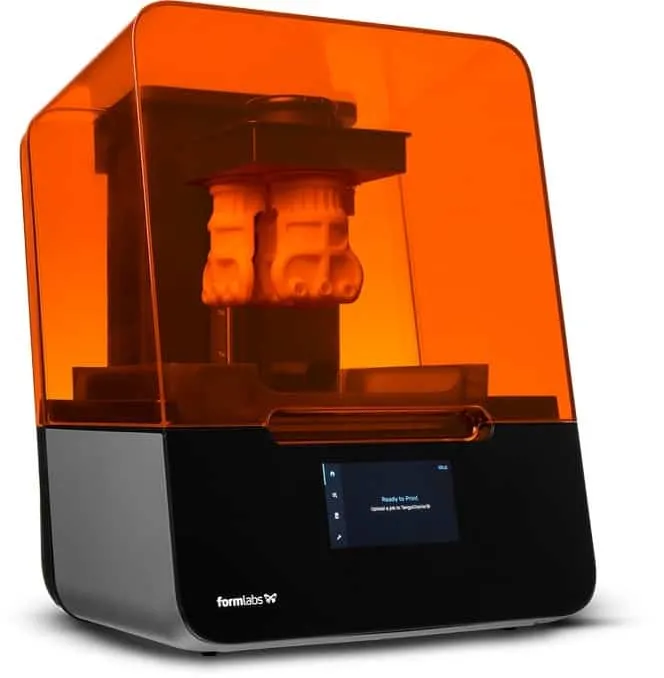

The FormLabs Form 3 is an excellent 3D printer that works fast and can give you models and molds printed with castable wax. It’s easy to use, with everything coming to you as a plug and play: no tweaking, no adjustments, and calibration required.
It does cost a lot of money, with prices starting at more than $3,000. But at that price, you will be rewarded with easy and fast printing times. Almost no clean-up is necessary.
Another thing you should know is that Form 3 is not an open-source printer when it comes to filaments. You will need to buy the resins from FormLabs, as well as other consumables such as the resin tank.
However, this printer gives you excellent prints. Fine details, smooth curves, almost burnished surfaces are what you get. It’s doesn’t look like it came from a 3D printer because the layers are not that visible.
This printer can print with resolutions of up to 25 micrometers. You can also send your prints via Wi-Fi.
Add the touchscreen that allows you to control the printer and the sizable print area of 5.7 by 5.7 by 7.3 inches (145 by 145 by 185 centimeters), and you have a serious contender for a wax 3D printer.
The Light Processing Unit (LPU) inside this printer uses a lens and mirror system to deliver accurate and repeatable prints with smooth surface finish, high detail, and incredible clarity.
What is Wax Material?
In chemistry, the wax is defined as a simple lipid made from long-chain alcohols and fatty acids combining together. There is a variety of specific types of waxes found in nature, the most common being the type that bees secrete. 3D printing uses the castable resin form of wax, which means the extra material in the wax cures it to make it harden after being manipulated into its final shape.
Waxes can be naturally occurring or synthetic, but because additive manufacturing is necessary to guide waxes’ behavior for fabrication purposes, 3D printing with wax tends to use the man-made stuff. So you won’t be 3D printing with pure wax, but your finished objects will have very similar properties to it once you’re done.3
How do you 3D print with wax?
3D printing with wax can be slightly more involved than working with traditional filaments like ABS or PLA. There is also more than one way to 3D print with wax; we’ll discuss each in detail so you can decide which will work better for your needs.
- Inkjet 3D printing with wax. First up is a 3D printing process that you will recognize as the most common type – the kind that uses filaments added onto themselves from an extruder from a programmed pattern to complete a finished object. This is the basis of additive 3D printing, and the concept for printing with wax is the same. However, the process of getting to that same end is different. Because wax is not firm enough to be spooled into the threadlike filaments you see with standard thermoplastics, it has to be heated and melted within the printer and then dripped onto the printer bed instead of fed through.
- The most common sub-process of inkjet 3D printing with wax is called drop on demand manufacturing. During this process, the material – in this case, wax – is deposited in tiny dots instead of a continuous line. DoD printers often have two extruder heads to supply the main printing material with dissolvable support material so that the final product can hold patterns with gaps and holes until the final object is hardened.
- Lost-wax casting 3D printing with wax. Another way to 3D print with wax involves using the wax as a mold – but not as an injection mold. Although that’s possible, that’s a very different process, and here we’re talking about the ability to make a wax mold that is printed in the exact shape of the object. This process is called lost-wax casting, and your first step is to create a 3D model of your object in your drafting software of choice. Then, you 3D print a wax model of the object. You cast a mold around the 3D wax model, and you melt the wax so that only the mold remains. Finally, you pour whatever surface finish material you want to use into the mold, let it harden, and dissolve the mold. A lot of fine jewelry makers in the jewelry industry use this process because it allows for one of the best levels of detail possible in 3D printing, and if any adjustments need to be made to the molds before the final step, it’s much easier to adjust on the computer and 3D print again than to manipulate the metal itself without damaging it.
Because its physical properties can shift more easily than materials rooted in firmer molecule bonds, you have to consider several general factors no matter which process you choose as your wax 3D printing preference.
So here are a few pros and cons to consider whether you’re looking to mold delicate metal shapes or just want to try wax as new material.
What are the pros of 3D printing with wax?
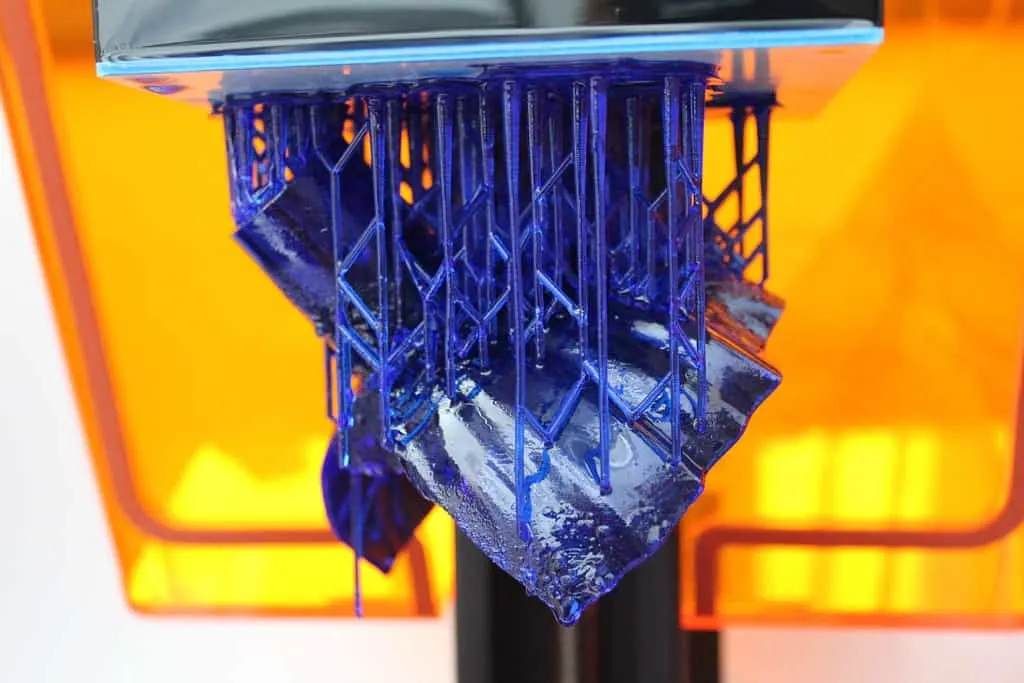
The finest layer of mold detail
Wax is most commonly used to create molds because of its stellar layer resolution of 0.025 mm. This is, frankly, the most amazing level of detail we’ve seen in 3D printing, especially in the area of molds and supportive materials.
And when used as molds for intricate yet delicate products like printed jewelry, the metal that fills the mold takes all that detail with it to the final product, something you could never achieve with the lower layer resolution of pretty much every other 3D printing material.
No need for different supportive material
3D printers that can use wax can print two wax types at the same time to produce supportive bracing as well as the 3D printed object itself. They do this by printing the wax at two different temperatures; the wax that melts at the higher temperature, about 70 degrees Celsius, is used for the object itself, and the wax that melts at a lower temperature creates the supportive material that bridges gaps in the wax patterns until the initial wax hardens. Then the supportive wax is melted off.
Variations of color and properties
Wax is thought of as a uniform range of beiges, yellows, and browns, but you can find 3D printable waxes in all sorts of colors, including those you can’t find in nature like neons. You can also find variations on wax’s general properties in different viscosities and different mixes of resin within the material to better suit the type of object or mold you want to create.
Easy melting points
Wax generally has a lower melting point than most other 3D printing materials. This makes it easier to use as a mold and supporting material, of course, since you can melt them off whatever they are upholding without worrying about melting the actual molded object itself. But it also means that wax 3D printers run cooler than other 3D printers, so you’re able to operate with a larger safety margin than polymers or thermoplastics that require extrusion temperatures over 100 degrees Celsius.
Insoluble in water
In nature, the wax is often excreted by leaves and other parts of plants to keep them from absorbing too much water in rainy areas of the world. Wax acts as a water protector for your 3D printing objects as well; it’s yet another reason why the material makes such a good mold.
It doesn’t dissolve in water, so if you need to use a water cooling process for molded metals before they’re ready to come out, the wax is the perfect way to hold the metal’s shape during that last step before breaking off of it easily to reveal the final product.
What are the cons of 3D printing with wax?
The inherent instability of material
The biggest drawback of working with wax to make any sort of solid final object is that you will not be able to use untreated wax on its own without putting your object in major danger of destruction. Since pure wax is so malleable and has such a low melting point, it’s crucial to know how to work with resins, UV light vulcanization, or other firming techniques to make it stiffer. Look for 3D printers with built-in UV lights and potentially invest in a resin / machinable wax filament drying unit like the PrintDry system.
Continue reading our full guide on how to find the best filament drying systems.
Temperature sensitive
Even with the assistance of finishing details such as these, the wax is difficult to use as material for a final product. It’s melting point is above room temperature by about 50 degrees Celsius, which sounds like a lot but can put your wax figures in more danger of warping if you aren’t able to control the temperature of the environment where you store them.
Can’t be extruded like spooled filaments
We’ve run across this trait in several other 3D printing materials, most notably chocolate and silicone, so wax is not the only thing that has to be melted into a liquid instead of threaded through an extruder. But this is worth mentioning as an extra burden on whoever is looking to 3D print with it.
Inkjet 3D printing is just as developed and discussed as traditional extruding, but it’s not a great place for the first time 3D printing enthusiast to start. Although it doesn’t mean learning a completely foreign skill, it does require a mastery of another branch of the process, so be prepared for that if you ever want to work with wax in a 3D printer.
Special equipment
This comes from the inkjet drop on demand process printing technology that best serves wax’s properties when 3D printing. We’ll discuss the specifics of what to look for to facilitate this below, but keep in mind this is a subsection of an already specialty process with the 3D printing world, so your ability to adjust to new things is crucial if you want to 3D print with wax.
If you aren’t willing to invest in more equipment explicitly made for a drop on demand or at least inkjet 3D printing, you won’t be able to get your wax to behave as it should. 3D printing with wax is an investment of both more time and money.
What do I need to look for in a 3D printer that can work with wax?

Now that we’ve gone over the details of 3D printing with wax, let’s list what you need to look for in a printer that can handle this process.
An inkjet or drop on demand 3D printing process.
Wax needs an additive process that will deposit it onto the printing bed, and both inkjet and drop on demand equipment can do that for you. They’re similar but not identical, so check the details on the specific printers you’re eyeing to see which one will work better for your needs.
An internal material heater is able to handle two temperatures at one time.
In its role as both a top-notch mold material and a support filament, wax can’t be both at the same temperature. Therefore you need to make sure the 3D printer you’re looking at can warm up your main object/mold wax at a higher temperature than your support system wax; it’s totally possible to find equipment that will do this, and when you do, you’ll be rewarded by a superhuman ability to create details without a trace of all the background props needed for that level of work.
UV vulcanizing chamber and light.
Is this absolutely necessary to process 3D printing with wax? No. Is this a good way to ensure any finished products you want to 3D print in wax stiffen so they aren’t as prone to damage? Yes. Is this the part of the 3D printing process that is most likely to turn into a science fiction movie starring Tom Cruise? You bet!
Additional materials to use in your 3D printed wax molds.
Although you can 3D print wax objects to be their own thing, 3D printing with wax goes to the next level when you use it to create molds for other materials. We strongly recommend trying this method if you work with small to medium objects in materials that are difficult to detail on their own, like precious metals. You will be blown away by the results, and you’ll even be able to go pro if that’s something you’ve wanted to do but haven’t had the capacity to reach for until now.
Quickly drying resin based filament is key to maintaining structural integrity. Particularly for wax-style filaments, we use this system to prevent ambient moisture from corrupting the filament.
Best Wax 3D Printing Services?
- Solidscape has a great variety of choices for you, no matter what kind of 3D printing process with wax you ultimately decide on.
- Sculpteo print on demand services are an excellent alternative if you don’t want to jump all in with your own 3D wax printing equipment. We understand – that can get expensive if you’re adding it to your current wares – and so does Sculpteo, so they’ll give you a taste on their own machines for less than setup costs for a new printer.
- EnvisionTec is all business with its line of printers designed to help you print multiple molds for custom designed jewelry or dental work at once. Their machines get a bit pricey for hobbyists, but they can’t be beaten for professionalism.
Finding a 3D wax printer shouldn’t be a major hassle no matter what you want to use it for. Use these details to find your best fit!
Dead simple to set-up, comes pre-assembled, intuitive touch-screen and exceptional level of detail. This machine empowers CREATORS, without expecting you to be a mechanic. The small - but precise - print bed is perfect for miniatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer: One of the most important uses of wax 3D printing is in the making of molds for jewelry. You can design a mold and save it as a 3D file, load the design on your 3D printer and wait for the model to be finished.
Once you have the wax model, you can build a mold around it and then melt the wax inside to create a hollow space. You can then pour the molten metal into the mold and wait for it to harden.
You now have created a new piece of jewelry. The design can be as intricate and complex as you want. You can also print models using wax-like filaments. These filaments have the same properties as wax.
Answer: It is possible to use precious metals in creating jewelry, but right now, most jewelers are using w3D printing to make molds where they can pour molten gold, silver, or other precious metals.
A wax 3D printer, in short, will replace the tedious process of hand carving the wax mold. If you want to 3D print using gold, you can invest in a direct metal laser sintering machine.
This machine can solidify gold powder using a lower. However, they cost around $150,000.
Answer: Printing with wax has a very similar process to printing with plastic filaments and resins. The printer will create the model layer by layer. As such, working times and the final results are nearly identical.
However, it’s easier to smooth out the surface of wax models. What’s more, you can use it when you want to cast metals, making it a suitable material for jewelry mold making. You can also use it for casting silicone.
Answer: Yes. A big factor for the significant difference in pricing is that castable wax is much more expensive than filaments and resin. Plus, the printing technology used is usually costlier than your standard FDM and SLS 3d printers.
To provide you a clear idea of how much it costs to print a using castable wax, we downloaded a darth vader ring design from Thhingiverse.com and submitted that to Craftcloud for an instant quote.
If you print that ring using castable wax on an MJP printer, you will need to pay $57,33. Compared to $8,80 for polypropylene using SLS printers and $9,25 for PLA using FDM printers, castable wax is more than six times more expensive.
Take Your 3D Printing to the Max with Wax 3D Printers
It is amazing just how 3D printing has improved over the years. We now have capable 3D printers that work with an amazing array of materials, from plastic to nylons, metals, and wax-like. As such, our workflows and processes are made even faster and easier.
Now that you know how wax 3D printing works, as well as some of the best printers and materials you should consider, why not give it a whirl?
Further Reading on Printing Materials and Applications
- How to Find the Best Titanium Metal 3D Printer
- How to Find the Best Silicone 3D Printer
- How to Find the Best Carbon 3D Printer
- How to Find the Best 3D Printer for Flexible Filament
- How to Find the Best Chocolate 3D Printer
- How to Find the Best 3D Printer for Miniatures
- Injection Molding vs 3D Printing
- Best Hotends for 3D Printers
- Anycubic Photon Review
- Anycubic Photon vs Elegoo Mars

![Best Wax 3D Printer and Wax Filament [2022]](https://total3dprinting.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/How-To-Find-The-Best-Wax-3D-Printer.png.webp)








